ವಿದ್ಯುಚ್ಛಕ್ತಿ ಮತ್ತು ಮಂಡಲಗಳು ಸಾರಾಂಶ -
• ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ಕೋಶವು ವಿದ್ಯುಚ್ಛಕ್ತಿಯ ಒಂದು ಆಕರ.
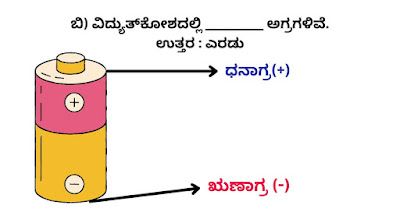
• ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ಕೋಶವು ಎರಡು ಅಗ್ರಗಳನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿದೆ; ಒಂದನ್ನು ಧನಾಗ್ರವೆಂದೂ (+) ಇನ್ನೊಂದನ್ನು ಋಣಾಗ್ರವೆಂದೂ (-) ಕರೆಯುವರು.
• ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಬಲ್ಬ್ ತಂತುವನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿದ್ದು ಅದು ಬಲ್ಬ್ನ ಅಗ್ರಗಳಿಗೆ ಜೋಡಿಸಲ್ಪಟ್ಟಿದೆ.
• ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಪ್ರವಾಹವು ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಬಲ್ಬ್ನ ಮೂಲಕ ಹರಿದಾಗ ಅದು ಬೆಳಗುತ್ತದೆ.
• ಮುಚ್ಚಿದ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಮಂಡಲದಲ್ಲಿ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಪ್ರವಾಹವು ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ಕೋಶದ ಒಂದು ಅಗ್ರದಿಂದ ಇನ್ನೊಂದು ಅಗ್ರಕ್ಕೆ ಹರಿಯುತ್ತದೆ.
• ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಮಂಡಲ ಪೂರ್ಣಗೊಳಿಸಲು ಅಥವಾ ಕಡಿತಗೊಳಿಸಲು ಬಳಸುವ ಸರಳ ಸಾಧನವೇ ಸ್ವಿಚ್.
• ತಮ್ಮ ಮೂಲಕ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ತನ್ನು ಹರಿಯಲು ಬಿಡುವ ಪದಾರ್ಥಗಳಿಗೆ ವಾಹಕಗಳೆನ್ನುವರು.
• ತಮ್ಮ ಮೂಲಕ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ತನ್ನು ಹರಿಯಲು ಬಿಡದ ಪದಾರ್ಥಗಳಿಗೆ ಅವಾಹಕಗಳೆನ್ನುವರು.
ವಿದ್ಯುಚ್ಛಕ್ತಿ ಮತ್ತು ಮಂಡಲಗಳು ಅಭ್ಯಾಸಗಳು
೧. ಬಿಟ್ಟ ಸ್ಥಳಗಳನ್ನು ತುಂಬಿ.
ಎ) ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಮಂಡಲವನ್ನು ಕಡಿತಗೊಳಿಸಲು ಬಳಸುವ ಸಾಧನ __________
ಉತ್ತರ : ಸ್ವಿಚ್
ಬಿ) ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ಕೋಶದಲ್ಲಿ _________ ಅಗ್ರಗಳಿವೆ.
ಉತ್ತರ : ಎರಡು
೨. ಈ ಕೆಳಗಿನ ಹೇಳಿಕೆಗಳನ್ನು ಸರಿ ಅಥವಾ ತಪ್ಪು ಎಂದು ಗುರುತು ಮಾಡಿ.
ಎ) ಲೋಹಗಳ ಮೂಲಕ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಪ್ರವಾಹ ಹರಿಯುತ್ತದೆ.
ಉತ್ತರ : ಸರಿ
ಬಿ) ಲೋಹದಿಂದ ಮಾಡಿದ ತಂತಿಗಳ ಬದಲು ಸೆಣಬಿನ ದಾರವನ್ನು ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಮಂಡಲ ರಚಿಸಲು ಬಳಸಬಹುದು.
ಉತ್ತರ : ತಪ್ಪು
ಸಿ) ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಪ್ರವಾಹವು ಥರ್ಮೊಕೋಲ್ ಹಾಳೆಯ ಮೂಲಕ ಪ್ರವಹಿಸಬಲ್ಲದು.
ಉತ್ತರ : ತಪ್ಪು
೩. ಚಿತ್ರ ೧೨.೧೩ರಲ್ಲಿ ತೋರಿಸಿರುವ ಜೋಡಣೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಬಲ್ಬ್ ಬೆಳಗುವುದಿಲ್ಲ ಏಕೆಂದು ವಿವರಿಸಿ.
ಉತ್ತರ : ಚಿತ್ರದಲ್ಲಿರುವ ಮಂಡಲದಲ್ಲಿ ಮಂಡಲವು ಪೂರ್ಣಗೊಂಡಿಲ್ಲ ಇಲ್ಲಿ ಸ್ಕ್ರೂ ಡ್ರೈವರ್ ನ ಹಿಡಿಕೆಯು ಅವಾಹಕ ವಸ್ತುವಾಗಿರುವುದರಿಂದ ಅದರ ಮೂಲಕ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಪ್ರವಹಿಸುವುದಿಲ್ಲ. ಅದರಿಂದ ಮಂಡಲವು ಪೂರ್ಣಗೊಳ್ಳದೆ ಬಲ್ಬ್ ಬೆಳಗುವುದಿಲ್ಲ.
೪. ಚಿತ್ರ ೧೨.೧೪ರಲ್ಲಿ ತೋರಿಸಿರುವ ಬಲ್ಬ್ ಬೆಳಗುವಂತೆ ಮಾಡಲು ಎರಡು ತಂತಿಗಳ ಸ್ವತಂತ್ರ ತುದಿಗಳನ್ನು ಎಲ್ಲಿಗೆ ಸೇರಿಸಬೇಕು ಎಂಬುದನ್ನು ಸೂಚಿಸುವಂತೆ ಚಿತ್ರವನ್ನು ಪೂರ್ಣಗೊಳಿಸಿ.
ಉತ್ತರ :
೫. ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಸ್ವಿಚ್ಚನ್ನು ಉಪಯೋಗಿಸುವ ಉದ್ದೇಶವೇನು? ಅಂತರ್ಗತ ಸ್ವಿಚ್ಚನ್ನು ಒಳಗೊಂಡಿರುವ ಕೆಲವು ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಉಪಕರಣಗಳನ್ನು ಹೆಸರಿಸಿ.
ಉತ್ತರ : ಮಂಡಲವನ್ನು ಪೂರ್ಣಗೊಳಿಸುವ ಅಥವಾ ಕಡಿತಗೊಳಿಸುವ ಸರಳ ಸಾಧನವೇ ಸ್ವಿಚ್ಛ. ಅಂತರ್ಗತ ಸ್ವಿಚ್ಚನ್ನು ಒಳಗೊಂಡಿರುವ ಕೆಲವು ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಉಪಕರಣಗಳೆಂದರೆ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಇಸ್ತ್ರೀ ಪೆಟ್ಟಿಗೆ, ರೆಫ್ರಿಜರೇಟರ್.
೬. ಚಿತ್ರ ೧೨.೧೪ರಲ್ಲಿ ತೋರಿಸಿರುವಂತೆ ಸೇಫ್ಟಿಪಿನ್ನ ಬದಲು ರಬ್ಬರ್ ಬಳಸಿ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಮಂಡಲವನ್ನು ಪೂರ್ಣಗೊಳಿಸಿದರೆ ಬಲ್ಬ್ ಬೆಳಗುವುದೇ?
ಉತ್ತರ : ರಬ್ಬರ್ ಒಂದು ಅವಾಹಕ ವಸ್ತುವಾಗಿರುವುದರಿಂದ ಅದನ್ನು ಮಂಡಲದಲ್ಲಿ ಬಳಸಿದರೆ ಮಂಡಲವು ಪೂರ್ಣಗೊಳ್ಳುವುದಿಲ್ಲ. ಅದರಿಂದ ಬಲ್ಬ್ ಬೆಳಗುವುದಿಲ್ಲ.
೭. ಚಿತ್ರ ೧೨.೧೫ರಲ್ಲಿ ತೋರಿಸಿರುವ, ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಮಂಡಲದಲ್ಲಿ ಬಲ್ಬ್ ಬೆಳಗುತ್ತದೆಯೇ?
ಉತ್ತರ : ಈ ಚಿತ್ರದಲ್ಲಿ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಮಂಡಲವು ಪೂರ್ಣಗೊಂಡಿರುವುದರಿಂದ ಬಲ್ಬ್ ಬೆಳಗುತ್ತದೆ.
೮. ಒಂದು ವಸ್ತುವಿನ ಮೇಲೆ ವಾಹಕ ಟೆಸ್ಟರ್ಅನ್ನು ಬಳಸಿದಾಗ ಬಲ್ಬ್ ಬೆಳಗುವುದು ಕಂಡುಬಂದಿತು. ಆ ವಸ್ತುವು ವಾಹಕವೇ ಅಥವಾ ಅವಾಹಕವೆ? ವಿವರಿಸಿ.
ಉತ್ತರ : ಬಲ್ಬ್ ಬೆಳಗಿರುವುದರಿಂದ ಆ ವಸ್ತುವು ವಾಹಕ. ಏಕೆಂದರೆ ವಾಹಕಗಳು ತಮ್ಮ ಮೂಲಕ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ನ್ನು ಹರಿಯಲು ಬಿಡುತ್ತವೆ. ಇದರಿಂದ ಬಲ್ಬ್ ಬೆಳಗುತ್ತದೆ.
೯. ನಿಮ್ಮ ಮನೆಯಲ್ಲಿರುವ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಸ್ವಿಚ್ಚನ್ನು ರಿಪೇರಿ ಮಾಡುವಾಗ ಇಲೆಕ್ಟ್ರಿಷಿಯನ್ ರಬ್ಬರ್ ಕೈಗವಸನ್ನು (GLOVES) ಏಕೆ ಬಳಸಬೇಕು? ವಿವರಿಸಿ.
ಉತ್ತರ : ರಬ್ಬರ್ ಒಂದು ಅವಾಹಕ ವಸ್ತುವಾಗಿರುವುದರಿಂದ ಅದು ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ನ್ನು ತನ್ನ ಮೂಲಕ ಹರಿಯಗೊಡುವುದಿಲ್ಲ, ಇದರಿಂದ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಸ್ವಿಚ್ಚನ್ನು ರಿಪೇರಿ ಮಾಡುವಾಗ ರಬ್ಬರ್ ಕೈಗವಸನ್ನು ಬಳಸುವುದರಿಂದ ಯಾವುದೇ ರೀತಿಯ ಅವಘಡಗಳು ಉಂಟಾಗುವುದಿಲ್ಲ.
೧೦. ಇಲೆಕ್ಟ್ರಿಷಿಯನ್ ರಿಪೇರಿ ಕೆಲಸಕ್ಕೆ ಬಳಸುವ ಇಕ್ಕಳ ಮತ್ತು ಸ್ಕ್ರೂ ಡ್ರೈವರ್ ಸಾಧನಗಳು ಪ್ಲಾಸ್ಟಿಕ್ ಅಥವಾ ರಬ್ಬರಿನ ಹೊದಿಕೆಯನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿರುತ್ತವೆ. ಏಕೆ? ನೀವು ವಿವರಿಸಬಲ್ಲಿರ?
ಉತ್ತರ : ಪ್ಲಾಸ್ಟಿಕ್ ಮತ್ತು ರಬ್ಬರ್ ಇವು ಅವಾಹಕ ವಸ್ತುಗಳಾಗಿರುವದರಿಂದ ಅವುಗಳ ತಮ್ಮ ಮೂಲಕ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ನ್ನು ಹರಿಯಗೊಡುವುದಿಲ್ಲ. ಯಾವುದೇ ರೀತಿಯ ವಿದ್ಯುತ್ ಅವಘಡಗಳು ಸಂಭವಿಸುವುದಿಲ್ಲ. ಆದ್ದರಿಂದ ಇಲೆಕ್ಟಿಷಿಯನ್ ರಿಪೇರಿ ಕೆಲಸಕ್ಕೆ ಬಳಸುವ ಇಕ್ಕಳ ಮತ್ತು ಸ್ಕ್ರೂ ಡ್ರೈವರ್ನಂತಹ ಸಾಧನಗಳು ಪ್ಲಾಸ್ಟಿಕ್ ಅಥವಾ ರಬ್ಬರಿನ ಹೊದಿಕೆಯನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿರುತ್ತದೆ.
Electricity and Circuits FAQs-
1. What is electricity?
Electricity is a form of energy resulting from the movement of charged particles, such as electrons.
2. How is electricity generated?
Electricity can be generated through various methods, including burning fossil fuels, and nuclear reactions, and harnessing renewable sources like wind, water, and sunlight.
3. What are conductors and insulators?
Conductors are materials that allow electricity to flow easily, like metals. Insulators are materials that resist the flow of electricity, such as rubber and plastic.
4. What is a circuit?
A circuit is a path that allows electricity to flow from a power source through various components and back to the source.
5. What is a closed circuit?
A closed circuit is a complete loop where electricity can flow continuously, powering devices along the way.
6. What is an open circuit?
An open circuit is a broken path where electricity cannot flow, leading to a lack of power in the circuit.
7. What is current in an electric circuit?
Current is the flow of electric charge (usually electrons) through a conductor. It's measured in amperes (A).
8. What unit is used to measure current?
Current is measured in amperes (A) or simply amps.
9. What is voltage?
Voltage is the electric potential difference between two points in a circuit, pushing the flow of electric charge.
10. What unit is used to measure voltage?
Voltage is measured in volts (V).
11. What is resistance?
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current in a circuit, caused by materials like wires and components.
12. How is resistance measured?
Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω).
13. What is Ohm's law?
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance between them:
I= V/R
14. What is a series circuit?
A series circuit is a circuit configuration where components are connected end-to-end, forming a single path for current to flow.
15. What is a parallel circuit?
A parallel circuit is a circuit configuration where components are connected across common points, providing multiple paths for current to flow.
16. How does a light bulb work in an electric circuit?
A light bulb works by heating a filament inside it, causing it to glow and emit light when current flows through it.
17. What is a battery?
A battery is a device that stores chemical energy and converts it into electrical energy, providing a power source for circuits.
18. How does a switch work in a circuit?
A switch controls the flow of electricity by opening or closing the circuit path, allowing you to turn devices on or off.
19. What is a fuse used for?
A fuse is a safety device that breaks the circuit if too much current flows through it, protecting the circuit from damage.
20. What is a circuit breaker?
A circuit breaker is an automatic switch that opens the circuit when there's a surge in current, preventing overloads and hazards.
21. What is a short circuit?
A short circuit occurs when two points in a circuit unintentionally connect, causing a large flow of current and potentially damaging the circuit.
22. What is static electricity?
Static electricity is the buildup of electric charges on the surface of objects due to friction or contact, which can lead to sparks or shocks.
23. How do magnets and electricity relate?
Moving electric charges create magnetic fields, and magnets can induce electric currents when they move relative to conductors.
24. What are the three main parts of a circuit?
The three main parts of a circuit are the power source (such as a battery), conductive path (wires), and load (devices using electricity).
25. How does a circuit with a capacitor behave differently?
A circuit with a capacitor store and releases electrical energy over time, providing a temporary energy source and affecting the circuit's timing and behavior.
KSEEB Solutions For Class 6 Science Chapters in kannada.
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ ೧ : ಆಹಾರ-ಇದು ಎಲ್ಲಿಂದ ದೊರಕುತ್ತದೆ?
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ ೪ : ಪದಾರ್ಥಗಳನ್ನು ಗುಂಪುಗಳಾಗಿ ವರ್ಗೀಕರಿಸುವುದು
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ ೫ : ಪದಾರ್ಥಗಳನ್ನು ಬೇರ್ಪಡಿಸುವಿಕೆ
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ ೬ : ನಮ್ಮ ಸುತ್ತಲಿನ ಬದಲಾವಣೆಗಳು
ಅಧ್ಯಾಯ ೭ : ಸಸ್ಯಗಳನ್ನು ತಿಳಿಯುವುದು

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.png)


PLEASE DO NOT ENTER ANY SPAM LINK IN THE COMMENT BOX