This article contains Class 10 Science MCQs Chapter 7 Control and Coordination to aid students in preparing for the board exam. Students may quickly answer the multiple-choice questions in this chapter by practicing the Control and Coordination MCQs. This will also help them score highly on the board exams. Therefore, students must first complete these tasks and then review the solutions that are given here. It will improve their exam readiness and provide them the confidence they need to take the board exams. For exam preparation, students can also access the NCERT/ CBSE Class 10 Science MCQs for other chapters.
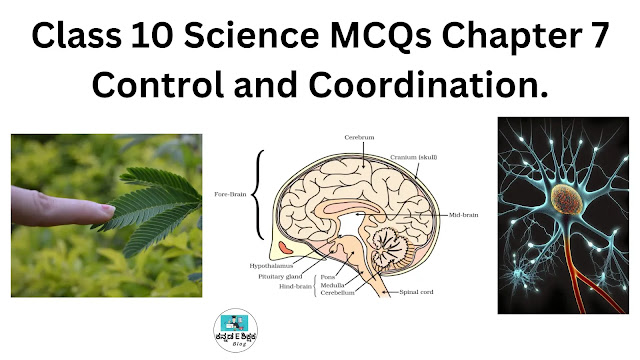
Class 10 Science MCQs Chapter 7 Control and Coordination.
1. The structural and functional units of the nervous system are:
(a) Neurons or nerve cells
(b) Neurotransmitters
(c) Synapses
(d) All of the above
Answer: (a) Neurons or nerve cells
Explanation: Neurons are the specialized cells of the nervous system that receive, process, and transmit information throughout the body through electrical and chemical signals. They are the basic building blocks of the nervous system and are responsible for all of its functions.
2. The nervous system includes:
(a) The brain
(b) The spinal cord
(c) Nerves
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Explanation: The nervous system is a complex network of organs and tissues that control all aspects of our bodies, from our thoughts and emotions to our movements and senses. The major components of the nervous system include the brain, the spinal cord, and nerves.
3. The other organ system for control and coordination of various life processes is the:
(a) Nervous system
(b) Endocrine system
(c) Cardiovascular system
(d) Digestive system
Answer: (b) Endocrine system
Explanation: The endocrine system is a complex network of glands that produce and release hormones, which are chemical messengers that regulate various bodily functions. Together with the nervous system, the endocrine system plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and controlling various life processes.
4. In plants, there is no centralized nervous system like in animals, but they do have a system of:
(a) Electrical signals
(b) Chemical signals
(c) Hormones
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Explanation: While plants lack a centralized nervous system like animals, they do have sophisticated mechanisms for sensing and responding to environmental stimuli. Plants use a combination of electrical signals, chemical signals, and hormones to coordinate their growth, development, and responses to various factors.
5. Chemical signaling in plants is mediated by:
(a) Light
(b) Touch
(c) Gravity
(d) Plant hormones
Answer: (d) Plant hormones
Explanation: Plant hormones, also known as phytohormones, are chemical messengers that play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes in plants, including growth, development, and responses to environmental stimuli. They act as signaling molecules that coordinate plant behavior and ensure their survival and adaptation to different environments.
6. Plants respond to a variety of stimuli, including:
(a) Light
(b) Touch
(c) Gravitational force
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Explanation: Plants exhibit a remarkable ability to sense and respond to a wide range of environmental stimuli, including light, touch, gravitational force, and chemical signals. These stimuli trigger various physiological and behavioral responses that allow plants to adapt to their surroundings and optimize their survival.
7. The function of control and coordination in plants is regulated by chemical substances known as:
(a) Plant hormones
(b) Neurotransmitters
(c) Synapses
(d) Sense organs
Answer: (a) Plant hormones
Explanation: Plant hormones, or phytohormones, are the primary regulators of control and coordination in plants. These signaling molecules act as chemical messengers, influencing various aspects of plant growth, development, and responses to environmental cues. They coordinate cellular activities and ensure the harmonious functioning of different plant organs.
8. Examples of plant hormones include:
(a) Auxins
(b) Gibberellins
(c) Cytokinins
(d) Abscisic acid (ABA)
(e) Ethylene
Answer: (e) All of the above
Explanation: Plant hormones encompass a diverse group of chemical messengers, each playing specific roles in regulating various aspects of plant physiology. Auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid (ABA), and ethylene are among the major classes of plant hormones, each with distinct functions and regulatory effects.
9. The movement of plants in the direction of stimulus is known as:
(a) Tropism
(b) Nastic movement
(c) Photoperiodism
(d) Phytochrome
Answer: (a) Tropism
Explanation: Tropism is a directional growth or movement response of plants in relation to an external stimulus. The stimulus can be light, gravity, water, or chemicals. Plants exhibit various types of tropisms, each with a specific stimulus and direction of response.
Phototropism: This is the movement of plants towards or away from light. For example, shoots of most plants exhibit positive phototropism, growing towards light sources.
Geotropism: This is the response of plants to gravity. Roots generally exhibit positive geotropism, growing downwards, while shoots exhibit negative geotropism, growing upwards.
Chemotropism: This is the movement of plants in response to chemical stimuli. Pollen tubes exhibit positive chemotropism, growing towards the ovules in the ovary.
Hydrotropism: This is the movement of plants in response to water. Roots generally exhibit positive hydrotropism, growing towards water sources.
Thigmotropism: This is the response of plants to touch or contact. Tendrils of climbing plants exhibit positive thigmotropism, coiling around support structures for climbing.
Nastic movements, on the other hand, are non-directional responses of plants, not necessarily related to a specific stimulus. They often involve changes in turgor pressure or cell elongation. Examples include the opening and closing of flowers, the folding of leaves at night, and the movement of carnivorous plant traps.
Photoperiodism is the physiological response of plants to the duration of light and darkness. It plays a crucial role in regulating flowering, dormancy, and other seasonal adaptations in plants.
Phytochrome is a pigment-protein that plays a central role in photoperiodism. It exists in two forms, Pr and Pfr, which absorb different wavelengths of light. The relative abundance of these forms determines the plant's response to light-dark cycles.
10. Coordination in animals is primarily mediated by the:
(a) Nervous system
(b) Endocrine system
(c) Muscular system
(d) Skeletal system
Answer: (a) Nervous system
Explanation: The nervous system is the primary control and coordination system in animals. It is responsible for receiving, processing, and transmitting information throughout the body, enabling animals to sense their surroundings, make decisions, and control their movements. The endocrine system, while playing an important role in regulating various bodily functions, operates on a slower timescale and complements the rapid communication and control provided by the nervous system.
The muscular system works in conjunction with the nervous system to produce movement. Muscles receive signals from nerves, which trigger contractions that generate force and movement. The skeletal system provides structural support and attachment points for muscles, allowing for coordinated and controlled movements.
11. Animals receive a variety of external information through specialized structures called:
(a) Sense organs
(b) Effectors
(c) Nerves
(d) Synapses
Answer: (a) Sense organs
Explanation: Sense organs, also known as receptors, are specialized structures that detect and transduce environmental stimuli into electrical signals. These signals are then processed by the nervous system, enabling animals to perceive their surroundings and respond accordingly. Examples of sense organs include photoreceptors for light, mechanoreceptors for touch, chemoreceptors for smell and taste, and auditory receptors for sound.
12. Sensory neurons are responsible for:
(a) Receiving information from sense organs
(b) Transmitting information to the brain
(c) Controlling muscles
(d) Producing hormones
Answer: (a) Receiving information from sense organs
Explanation: Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are specialized nerve cells that receive information from sense organs and transmit it to the central nervous system. They play a crucial role in converting sensory stimuli into electrical signals that can be processed and interpreted by the brain.
13. Motor neurons are responsible for:
(a) Receiving information from the brain
(b) Transmitting information to effector organs
(c) Receiving information from sense organs
(d) Producing hormones
Answer: (b) Transmitting information to effector organs
Explanation: Motor neurons, also known as efferent neurons, are specialized nerve cells that transmit signals from the central nervous system to effector organs, such as muscles and glands. They play a crucial role in coordinating movement and regulating various physiological functions.
14. The vertebrate nervous system is composed of:
(a) The brain and spinal cord
(b) The central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
(c) The autonomic nervous system and somatic nervous system
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Explanation: The vertebrate nervous system is a complex network of interconnected structures that control and coordinate all aspects of an animal's body. It is divided into two major components:
Central nervous system (CNS): The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brain is the primary organ for processing information, while the spinal cord serves as a relay center for signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
Peripheral nervous system (PNS): The PNS consists of nerves that connect the CNS to various organs, muscles, and sensory receptors throughout the body. It is responsible for transmitting sensory information to the CNS and motor commands from the CNS to effector organs.
15. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for:
(a) Controlling voluntary movements
(b) Regulating involuntary functions
(c) Receiving information from sense organs
(d) Transmitting signals to muscles
Answer: (b) Regulating involuntary functions
Explanation: The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is a division of the PNS that controls involuntary functions, such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and respiration. It operates independently of conscious control, maintaining homeostasis and ensuring the proper functioning of internal organs.
16. The somatic nervous system is responsible for:
(a) Controlling voluntary movements
(b) Regulating involuntary functions
(c) Receiving information from sense organs
(d) Transmitting signals to muscles
Answer: (a) Controlling voluntary movements
Explanation: The somatic nervous system (SNS) is another division of the PNS that controls voluntary movements. It allows us to consciously control our muscles, enabling actions such as walking, talking, and manipulating objects. The SNS receives information from sensory receptors and transmits signals to muscles, coordinating our actions and responses to external stimuli.
17. The human brain is the largest and most complex organ in the body.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The human brain is the most complex organ in the human body, containing billions of neurons and trillions of connections. It is responsible for all aspects of human consciousness, thought, emotion, memory, and behavior. Its intricate structure and vast network of interconnected neurons enable us to perceive, learn, remember, and respond to the world around us.
18. The functional junction between neurons is called a:
(a) Synapse
(b) Dendrite
(c) Axon
(d) Myelin sheath
Answer: (a) Synapse
Explanation: A synapse is the specialized junction between neurons that allows for the transmission of electrical and chemical signals. It is the fundamental unit of communication in the nervous system, enabling neurons to exchange information and coordinate their activity.
19. The information passing through neurons is in the form of:
(a) Chemical and electrical signals
(b) Electrical signals only
(c) Chemical signals only
(d) Mechanical signals
Answer: (a) Chemical and electrical signals
Explanation: Neurons transmit information through a combination of electrical and chemical signals. Electrical signals travel along the axon of a neuron, while chemical signals, called neurotransmitters, are released at synapses to activate or inhibit the receiving neuron.
20. What is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system?
A) Hormones
B) Neurons
C) Receptors
D) Synapses
Answer: B) Neurons
Explanation: Neurons, or nerve cells, are the structural and functional units of the nervous system.
21. Which plant hormone is responsible for regulating growth and development in plants?
A) Insulin
B) Auxins
C) Adrenaline
D) Thyroxin
Answer: B) Auxins
Explanation: Auxins play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes in plants, including growth and development.
22. What is the term for the movement of plants in response to a chemical stimulus?
A) Phototropism
B) Geotropism
C) Chemotropism
D) Nastic movement
Answer: C) Chemotropism
Explanation: Chemotropism is the movement of plants in response to a chemical stimulus.
23. What regulates flowering and seed germination in plants?
A) Phototropism
B) Phytochrome
C) Geotropism
D) Auxins
Answer: B) Phytochrome
Explanation: Phytochrome, small pigments in plants, regulates flowering and seed germination in response to the duration of light.
24. Which part of the brain is responsible for movement and posture coordination?
A) Cerebrum
B) Pons
C) Cerebellum
D) Medulla oblongata
Answer: C) Cerebellum
Explanation: The cerebellum is involved in movement and posture coordination.
25. What is the functional junction between neurons called?
A) Synapse
B) Dendrite
C) Axon
D) Myelin sheath
Answer: A) Synapse
Explanation: The synapse is the functional junction between neurons.
26. Which region of the brain includes the cerebrum and olfactory lobes?
A) Forebrain
B) Middle brain
C) Hindbrain
D) Spinal cord
Answer: A) Forebrain
Explanation: The forebrain includes the cerebrum and olfactory lobes.
27. What is the term for an unconscious and involuntary response to a stimulus, such as the sudden withdrawal of hands from touching a hot object?
A) Reflex action
B) Tropism
C) Chemotropism
D) Phototropism
Answer: A) Reflex action
Explanation: Reflex action is an unconscious and involuntary response to a stimulus.
28. Which gland is responsible for the regulation of blood calcium and phosphate levels?
A) Pituitary gland
B) Thyroid gland
C) Adrenal gland
D) Parathyroid gland
Answer: D) Parathyroid gland
Explanation: The parathyroid gland regulates blood calcium and phosphate levels.
29. What is the role of vasopressin in the body?
A) Regulation of water and electrolyte balance
B) Regulation of blood pressure
C) Stimulation of muscle contractions
D) Control of metabolic processes
Answer: A) Regulation of water and electrolyte balance
Explanation: Vasopressin is involved in the regulation of water and electrolyte balance in the body.
30. Which part of the brain is responsible for the regulation of respiration?
A) Cerebrum
B) Pons
C) Medulla oblongata
D) Cerebellum
Answer: B) Pons
Explanation: The pons is involved in the regulation of respiration.
31. What is the term for the recording of the electrical activity of the brain?
A) Echocardiogram
B) Electroencephalogram (EEG)
C) Electrocardiogram (ECG)
D) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Answer: B) Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Explanation: EEG is used to record the electrical activity of the brain.
32. Which hormone is responsible for the regulation of metabolism of carbohydrate, fat, and protein?
A) Insulin
B) Thyroxin
C) Adrenaline
D) Prolactin
Answer: B) Thyroxin
Explanation: Thyroxin, produced by the thyroid gland, regulates the metabolism of carbohydrate, fat, and protein.
33. What is the main function of the autonomic nervous system?
A) Control and integration of internal organs
B) Voluntary muscle movement
C) Regulation of sensory perception
D) Coordination of reflex actions
Answer: A) Control and integration of internal organs
Explanation: The autonomic nervous system mainly controls and integrates the function of internal organs.
34. What is the role of oxytocin in the body?
A) Regulation of water balance
B) Stimulation of muscle contractions and childbirth
C) Regulation of blood pressure
D) Control of metabolic processes
Answer: B) Stimulation of muscle contractions and childbirth
Explanation: Oxytocin stimulates contractions of smooth muscles, including those involved in childbirth.
35. Which part of the brain is involved in the regulation of swallowing, coughing, sneezing, and vomiting?
A) Pons
B) Cerebellum
C) Medulla oblongata
D) Cerebrum
Answer: C) Medulla oblongata
Explanation: The medulla oblongata regulates activities such as swallowing, coughing, sneezing, and vomiting.
36. What is the function of the hormones insulin and glucagon?
A) Regulation of blood pressure
B) Regulation of blood glucose levels
C) Stimulation of muscle growth
D) Control of heart rate
Answer: B) Regulation of blood glucose levels
Explanation: Insulin lowers blood glucose levels, while glucagon increases them.
37. Which gland is responsible for the secretion of growth hormones and tropic hormones that regulate other endocrine glands?
A) Thyroid gland
B) Adrenal gland
C) Pituitary gland
D) Pancreas
Answer: C) Pituitary gland
Explanation: The pituitary gland secretes growth hormones and tropic hormones that regulate other endocrine glands.
38. What is the primary male sex hormone responsible for the development of male accessory sex organs and secondary sexual characteristics?
A) Estrogen
B) Progesterone
C) Testosterone
D) Prolactin
Answer: C) Testosterone
Explanation: Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone responsible for the development of male accessory sex organs and secondary sexual characteristics.
39. Which part of the brain is protected by the bony box in the skull called the cranium?
A) Hindbrain
B) Forebrain
C) Middle brain
D) Cerebrum
Answer: D) Cerebrum
Explanation: The cranium protects the brain, which includes the cerebrum.
40. What is the space between the three membranes covering the brain called?
A) Cerebrospinal space
B) Meningeal space
C) Synaptic space
D) Ventricular space
Answer: B) Meningeal space
Explanation: The space between the meninges, the three membranes covering the brain, is known as the meningeal space.
41. Which hormone is responsible for the regulation of the mammary gland's function?
A) Vasopressin
B) Prolactin
C) Oxytocin
D) Thyroxin
Answer: B) Prolactin
Explanation: Prolactin regulates the function of the mammary gland.
42. What is the term for the movement of plant parts in response to touch or contact?
A) Phototropism
B) Geotropism
C) Thigmotropism
D) Chemotropism
Answer: C) Thigmotropism
Explanation: Thigmotropism is the movement of plant parts in response to touch or contact.
43. Which hormone is responsible for the regulation of female accessory sex organs and secondary sexual characteristics in females?
A) Estrogen
B) Progesterone
C) Testosterone
D) Oxytocin
Answer: A) Estrogen
Explanation: Estrogen regulates female accessory sex organs and secondary sexual characteristics in females.
44. What is the role of the spinal cord in the nervous system?
A) Regulation of respiration
B) Coordination of muscle movements
C) Transmission of nerve impulses
D) Regulation of hormonal balance
Answer: C) Transmission of nerve impulses
Explanation: The spinal cord is involved in the transmission of nerve impulses.
45. Which hormone is responsible for the regulation of water and electrolyte balance in the body?
A) Thyroxin
B) Vasopressin
C) Insulin
D) Adrenaline
Answer: B) Vasopressin
Explanation: Vasopressin regulates water and electrolyte balance in the body.
46. What is the purpose of the endocrine system in animals?
A) Coordination of movement
B) Control of sensory perception
C) Regulation and coordination of body functions using hormones
D) Transmission of electrical signals
Answer: C) Regulation and coordination of body functions using hormones
Explanation: The endocrine system regulates and coordinates body functions using hormones.
48. Which hormone regulates the growth and development of bones and muscles?
A) Thyroxin
B) Insulin
C) Growth hormone
D) Adrenaline
Answer: C) Growth hormone
Explanation: Growth hormone regulates the growth and development of bones and muscles.
49. What is the role of the hypothalamus in the endocrine system?
A) Secretion of hormones
B) Regulation of the pituitary gland
C) Control of blood pressure
D) Coordination of muscle movements
Answer: B) Regulation of the pituitary gland
Explanation: The hypothalamus regulates the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland.
50. What is the term for the movement of plants in response to gravity?
A) Phototropism
B) Geotropism
C) Thigmotropism
D) Chemotropism
Answer: B) Geotropism
Explanation: Geotropism is the movement of plants in response to gravity.
51. What is the term for the recording of the electrical activity of the heart?
A) Electroencephalogram (EEG)
B) Electrocardiogram (ECG)
C) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
D) Computed Tomography (CT) scan
Answer: B) Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Explanation: An ECG is used to record the electrical activity of the heart.
52. Which hormone is responsible for the regulation of blood pressure, heart rate, and carbohydrate metabolism?
A) Adrenaline
B) Insulin
C) Thyroxin
D) Vasopressin
Answer: A) Adrenaline
Explanation: Adrenaline regulates blood pressure, heart rate, and carbohydrate metabolism.
53. What is the term for the unconscious and involuntary response of effectors to a stimulus?
A) Tropism
B) Photoperiodism
C) Reflex action
D) Chemotropism
Answer: C) Reflex action
Explanation: Reflex action is the unconscious and involuntary response of effectors to a stimulus.
54. Which hormone regulates the maintenance of pregnancy and the development of mammary glands in females?
A) Estrogen
B) Progesterone
C) Testosterone
D) Prolactin
Answer: B) Progesterone
Explanation: Progesterone regulates the maintenance of pregnancy and the development of mammary glands in females.
55. What is the primary function of insulin in the body?
A) Lowering blood glucose levels
B) Increasing blood glucose levels
C) Regulating blood pressure
D) Stimulating muscle contractions
Answer: A) Lowering blood glucose levels
Explanation: Insulin lowers blood glucose levels.
56. Which part of the nervous system transmits information from sense organs to the brain?
A) Motor neurons
B) Interneurons
C) Sensory neurons
D) Synapses
Answer: C) Sensory neurons
Explanation: Sensory neurons transmit information from sense organs to the brain.
57. What is the function of the cerebrum in the brain?
A) Regulation of respiration
B) Coordination of muscle movements
C) Reception of information from sense organs
D) Regulation of hormonal balance
Answer: C) Reception of information from sense organs
Explanation: The cerebrum has sensory areas where information is received from sense organs.
58. What is the purpose of the central nervous system?
A) Coordination of internal organs
B) Integration of sensory information
C) Regulation of hormonal balance
D) Control of voluntary muscle movements
Answer: B) Integration of sensory information
Explanation: The central nervous system integrates sensory information.
59. Which hormone is responsible for the regulation of blood calcium and phosphate levels?
A) Insulin
B) Thyroxin
C) Parathyroid hormone
D) Adrenaline
Answer: C) Parathyroid hormone
Explanation: Parathyroid hormone regulates blood calcium and phosphate levels.
60. What is the role of the meninges in protecting the brain?
A) Regulation of hormone secretion
B) Transmission of nerve impulses
C) Mechanical protection
D) Coordination of muscle movements
Answer: C) Mechanical protection
Explanation: The meninges provide mechanical protection to the brain.
61. What is the term for the movement of plant parts in response to light?
A) Geotropism
B) Phototropism
C) Chemotropism
D) Thigmotropism
Answer: B) Phototropism
Explanation: Phototropism is the movement of plant parts in response to light.
62. Which part of the brain is involved in the coordination of voluntary muscle movements?
A) Cerebellum
B) Medulla oblongata
C) Pons
D) Cerebrum
Answer: A) Cerebellum
Explanation: The cerebellum is involved in the coordination of voluntary muscle movements.
63. What is the function of the peripheral nervous system?
A) Integration of sensory information
B) Control of voluntary muscle movements
C) Coordination of internal organs
D) Transmission of nerve impulses between the central nervous system and other parts of the body
Answer: D) Transmission of nerve impulses between the central nervous system and other parts of the body
Explanation: The peripheral nervous system transmits nerve impulses between the central nervous system and other parts of the body.
64. Which hormone is responsible for the regulation of the sleep-wake cycle and other daily rhythms in the body?
A) Melatonin
B) Cortisol
C) Growth hormone
D) Oxytocin
Answer: A) Melatonin
Explanation: Melatonin regulates the sleep-wake cycle and other daily rhythms in the body.
65. What is the role of the olfactory receptors in animals?
A) Regulation of blood pressure
B) Reception of sound stimuli
C) Detection of smells
D) Coordination of muscle movements
Answer: C) Detection of smells
Explanation: Olfactory receptors are responsible for the detection of smells in animals.
66. Which hormone is responsible for the regulation of the body's response to stress, including the "fight or flight" response?
A) Insulin
B) Adrenaline
C) Thyroxin
D) Estrogen
Answer: B) Adrenaline
Explanation: Adrenaline regulates the body's response to stress, including the "fight or flight" response.
67. What is the function of the endocrine glands in the human body?
A) Transmission of electrical signals
B) Coordination of voluntary muscle movements
C) Secretion of hormones directly into the bloodstream
D) Regulation of respiration
Answer: C) Secretion of hormones directly into the bloodstream
Explanation: Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream for regulation and coordination.
68. Which part of the brain is responsible for basic life functions such as heartbeat and breathing?
A) Cerebrum
B) Pons
C) Cerebellum
D) Medulla oblongata
Answer: D) Medulla oblongata
Explanation: The medulla oblongata is responsible for basic life functions such as heartbeat and breathing.
69. What is the primary function of the spinal cord in the nervous system?
A) Regulation of hormonal balance
B) Transmission of nerve impulses
C) Coordination of muscle movements
D) Control of voluntary muscle movements
Answer: B) Transmission of nerve impulses
Explanation: The spinal cord is primarily involved in the transmission of nerve impulses.
70. Which sense organ is responsible for the reception of sound stimuli?
A) Olfactory receptors
B) Photoreceptors
C) Gustatory receptors
D) Auditory receptors
Answer: D) Auditory receptors
Explanation: Auditory receptors are responsible for the reception of sound stimuli.
Yes/No Questions for Class 10 Science Control and Coordination with Answers👇👇
1. The axon conducts impulses away from the cell body to another neuron or tissue through synapses.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The axon is a long, slender fiber that extends from the cell body of a neuron and transmits electrical signals away from the cell body to another neuron or tissue through synapses. It is the primary output channel of a neuron, responsible for conveying information to other parts of the nervous system or effector organs.
2. The human brain is protected by the bony box in the skull called the cranium.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The cranium, also known as the skullcap, is the bony structure that encases and protects the brain. It provides a strong, protective barrier against external forces and trauma, ensuring the delicate brain is shielded from harm.
3. The brain is covered by three membranes called meninges.
(a) True
b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The meninges are three layers of protective membranes that surround and support the brain and spinal cord. They provide a physical barrier, regulate the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, and nourish the nervous tissue. The three layers are:
Dura mater: The outermost layer, tough and fibrous, providing structural support.
Arachnoid mater: A middle layer, delicate and web-like, containing cerebrospinal fluid.
Pia mater: The innermost layer, closely attached to the brain and spinal cord, providing nutrients and blood vessels.
4. The space between meninges is filled by cerebrospinal fluid that protects the brain from mechanical shocks.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless liquid that fills the space between the meninges and bathes the brain and spinal cord. It provides several essential functions, including:
Cushioning and shock absorption: CSF acts as a protective buffer, absorbing mechanical shocks and preventing damage to the delicate brain tissue.
Nutrient transport: CSF carries nutrients and oxygen to the brain and spinal cord, supporting their metabolic needs.
Waste removal: CSF helps remove metabolic waste products from the brain and spinal cord, maintaining a healthy environment for neuronal function.
5. The brain is broadly divided into three regions:
(a) Forebrain
(b) Middle brain
(c) Hindbrain
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
Explanation: The brain is a complex organ with a highly organized structure. It is broadly divided into three main regions:
Forebrain: The largest and most complex part of the brain, responsible for higher-order functions such as consciousness, thought, memory, and emotion.
Middle brain: A relay center for sensory information and motor commands, connecting the forebrain and hindbrain.
Hindbrain: Responsible for basic functions such as coordination, balance, and regulation of vital processes like heart rate and respiration.
6. The forebrain includes the cerebrum and olfactory lobes.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The forebrain is the largest and most highly developed part of the brain, responsible for our most complex cognitive abilities. It includes two major structures:
Cerebrum: The two hemispheres of the cerebrum are divided into lobes with specialized functions, including sensory processing, motor control, language, memory, and higher-order thought.
Olfactory lobes: These small structures are responsible for processing smell, the only sense that directly reaches the brain without passing through the thalamus.
7. The cerebrum is the most complex and specialized part of the brain.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The cerebrum, the largest part of the brain, is responsible for our most complex cognitive abilities, including:
Sensory processing: Receiving, interpreting, and integrating sensory information from various parts of the body.
Motor control: Planning, executing, and coordinating movements.
Language: Understanding, producing, and using language for communication.
Memory: Forming, storing, and retrieving information and experiences
Higher-order thought: Reasoning, problem-solving, decision-making, creativity, and consciousness.
The cerebrum is divided into two hemispheres, each with specialized functions. The left hemisphere typically controls language, logic, and analytical thinking, while the right hemisphere dominates spatial awareness, emotions, and creativity.
8. The hindbrain includes the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The hindbrain is the most posterior part of the brain, responsible for basic functions essential for survival. It includes three major structures:
Cerebellum: Coordinates movement, balance, and posture.
Pons: Involved in relaying sensory information and motor commands, as well as regulating sleep and respiration.
Medulla oblongata: Controls vital functions such as heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, and swallowing.
9. The medulla oblongata regulates swallowing, coughing, sneezing, and vomiting.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The medulla oblongata, located at the base of the brain, serves as a control center for several involuntary processes, including:
Swallowing: Regulates the coordinated movement of muscles involved in swallowing, ensuring food passes safely from the mouth to the esophagus.
Coughing: Initiates the forceful expulsion of air from the lungs to clear irritants or mucus.
Sneezing: Triggers the sudden expulsion of air from the nose and mouth to expel irritants or foreign particles.
Vomiting: Coordinates the contractions of abdominal muscles and relaxation of esophageal sphincters to forcefully expel stomach contents.
These involuntary reflexes are essential for maintaining airway clearance, protecting the body from harmful substances, and regulating various bodily functions.
10. The pons plays a role in the regulation of respiration.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The pons, located between the forebrain and medulla oblongata, plays a crucial role in regulating respiration, the process of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the environment. It contains respiratory centers that control the rhythm and depth of breathing.
11. The cerebellum coordinates movement and posture.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The cerebellum, located at the back of the brain, is responsible for coordinating movement and maintaining posture. It receives information from sensory receptors, motor areas of the brain, and the vestibular system, which senses balance and spatial orientation. The cerebellum integrates this information and sends signals to the motor system, fine-tuning movements, ensuring smooth coordination, and maintaining balance.
12. The spinal cord is also surrounded by meninges.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The spinal cord, like the brain, is surrounded by three layers of meninges: the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. These protective membranes provide a physical barrier, regulate cerebrospinal fluid flow, and nourish the nervous tissue.
13. The autonomic nervous system is primarily responsible for controlling and integrating the function of internal organs like the heart, blood vessels, glands, smooth muscles, and uterus in the body.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions, such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, respiration, and reproductive processes. It operates independently of conscious control, ensuring the proper functioning of internal organs and maintaining homeostasis. The ANS is divided into two main branches:
Sympathetic nervous system: Responsible for the "fight-or-flight" response, mobilizing the body for action in stressful or emergency situations.
Parasympathetic nervous system: Responsible for the "rest-and-digest" response, conserving energy and promoting relaxation when the body is at rest or in a safe environment.
The ANS maintains a delicate balance between these two opposing systems, ensuring that the body adapts to changing
14. EEG (Electro Encephalogram) can record the electrical activity of the brain.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a non-invasive medical test that records the electrical activity of the brain. It measures the voltage fluctuations generated by neurons firing in the brain, providing insights into brain function and activity. EEG is used to diagnose various neurological disorders, such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, and brain tumors.
15. Reflection action is an unconscious and involuntary response of effectors to stimulus.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: Reflex actions are rapid, involuntary responses to stimuli that do not involve conscious thought or decision-making. They are mediated by reflex arcs, neural pathways that connect sensory receptors to effector organs through the spinal cord or lower brain centers. Reflexes are essential for survival and protection, allowing us to react quickly to danger or threats.
Examples of reflex actions include withdrawing a hand from a hot object, blinking to protect the eyes from foreign particles, and sneezing or coughing to expel irritants.
16. Hormones are chemical substances secreted in trace amounts by specialized tissues called endocrine glands.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: Hormones are chemical messengers secreted by endocrine glands, which are ductless glands that release their hormones directly into the bloodstream. Hormones travel throughout the body, binding to specific receptors on target cells to exert their physiological effects. They regulate a wide range of bodily functions, including growth, development, metabolism, reproduction, and stress response.
17. The term hormones was introduced by Bayliss and Stasling.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The term "hormone" was coined by British physiologists William Bayliss and Ernest Starling in 1902. They proposed the concept of chemical messengers produced by organs and transported by the blood to influence the activity of distant tissues. This laid the foundation for the study of endocrinology, the branch of biology that investigates hormones and their roles in the body.
18. Hormones are specific chemical messengers.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: Hormones are highly specific chemical messengers that bind to specific receptors on target cells. This specificity ensures that hormones only exert their effects on the intended tissues, avoiding unwanted interactions with other cells. The structure of a hormone determines its receptor affinity, influencing its ability to bind and activate the receptor.
19. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: Endocrine glands are specialized tissues that produce and release hormones directly into the bloodstream. They are ductless glands, lacking ducts that connect them to other organs or the external environment. Hormones, once released into the blood, travel throughout the body, reaching target cells that express the appropriate receptors.
20. Hormones are poured directly into the blood and carried by blood circulation.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: Endocrine glands release hormones into the bloodstream, allowing them to travel throughout the body and reach target tissues. The circulatory system acts as a delivery system, transporting hormones to their intended destinations. This enables hormones to exert their effects on cells that may be located far from the endocrine gland that produced them.
21. Hormones act on specific tissues/organs called target organs.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: Hormones exert their effects on specific tissues/organs called target organs. Target organs express receptors that can bind to the hormone, allowing the hormone to trigger a specific cellular response. The presence or absence of these receptors determines which cells will be affected by the hormone.
Different hormones have different target tissues, reflecting their diverse functions in the body. For instance, insulin targets cells involved in glucose uptake, while thyroid hormones target cells involved in metabolism and growth.
I hope this is helpful. Please let me know if you have any other questions.
22. Hormones can be classified into different types based on their chemical structure.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: Hormones can be classified into different types based on their chemical structure. The major classes of hormones include:
Steroid hormones: These hormones are derived from cholesterol and are soluble in lipids. They can easily diffuse across cell membranes and bind to receptors inside the cell nucleus, directly regulating gene expression. Examples include cortisol, aldosterone, and sex hormones.
Protein and peptide hormones: These hormones are composed of amino acids and are water-soluble. They cannot directly enter cells but bind to receptors on the cell surface, triggering signaling pathways that lead to cellular responses. Examples include insulin, glucagon, and growth hormone.
Amine hormones: These hormones are derived from amino acids and are water-soluble. They also bind to receptors on the cell surface, activating signaling pathways that influence cellular function. Examples include epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and thyroid hormones.
23. The pituitary gland is known as the master gland of the endocrine system.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain, is often referred to as the "master gland" of the endocrine system. It produces a variety of hormones that regulate the activity of other endocrine glands, including the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and gonads. The pituitary gland plays a crucial role in controlling growth, development, metabolism, and reproduction.
24. The thyroid gland is located in the neck and produces thyroid hormones.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the lower front of the neck. It produces two main hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones regulate metabolism, growth, and development.
25. The pancreas is located behind the stomach and produces insulin and glucagon.
() True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The pancreas is an elongated organ located behind the stomach. It plays a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels by producing two hormones: insulin and glucagon. Insulin lowers blood sugar by promoting glucose uptake into cells, while glucagon raises blood sugar by stimulating glucose release from the liver.
26. The adrenal glands are located on top of the kidneys and produce cortisol and aldosterone.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The adrenal glands are small, triangular glands located on top of the kidneys. They produce a variety of hormones, including cortisol and aldosterone. Cortisol is involved in regulating stress response, metabolism, and immune function. Aldosterone helps regulate blood pressure and fluid balance.
27. The gonads are the reproductive glands that produce sex hormones.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The gonads are the reproductive glands that produce sex hormones. In females, the gonads are the ovaries, which produce estrogen and progesterone. In males, the gonads are the testes, which produce testosterone. Sex hormones play a crucial role in sexual development, reproduction, and secondary sex characteristics.
28. The hypothalamus is a part of the brain that plays a crucial role in regulating hormone production and secretion.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: The hypothalamus, located at the base of the brain, serves as a central control center for the endocrine system. It receives signals from various parts of the brain and body, integrating this information to regulate the release of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus also directly produces hormones that control aspects of reproduction, thirst, appetite, and sleep-wake cycles.
29. Negative feedback is a common mechanism in hormone regulation.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: Negative feedback is a common regulatory mechanism in the endocrine system. It involves the detection of a hormone's effect and the subsequent suppression of its further production. This feedback loop helps maintain homeostasis by preventing hormone levels from becoming too high or too low.
For example, when blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas releases insulin to lower them. As blood sugar levels decrease, insulin secretion also decreases, preventing excessive blood sugar reduction. This negative feedback loop ensures that blood sugar levels are maintained within a normal range.
30. Hormones can act synergistically or antagonistically.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: Hormones can interact with each other in various ways, sometimes producing synergistic or antagonistic effects. Synergistic hormones work together to produce a combined effect that is greater than the sum of their individual effects. For instance, insulin and glucagon work together to regulate blood sugar levels.
Antagonistic hormones, on the other hand, counteract each other's effects. For example, epinephrine (adrenaline) and acetylcholine have opposing effects on heart rate and blood pressure. Epinephrine increases heart rate and blood pressure, while acetylcholine decreases them.
31. Hormones play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body.
(a) True
(b) False
Answer: (a) True
Explanation: Hormones are essential for maintaining homeostasis, the body's ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. They regulate a wide range of physiological processes, including metabolism, reproduction, growth, and stress response, ensuring that the body's internal conditions remain within a healthy range.
Hormones act as signaling molecules, coordinating the activities of different organs and systems to maintain homeostasis. They respond to changes in the body's internal environment and trigger adjustments to restore balance. Dysfunctions in the endocrine system can lead to imbalances in hormone levels, disrupting homeostasis and contributing to various health problems.
Dear readers above-provided Class 10 Science MCQs Chapter 7 Control and Coordination will play a very crucial role in your examination preparation. Please share with your all friends and if you have any doubts regarding the above mcqs please comment. Happy Reading.For more-👇👇👇 click here
What are the main topics of control and coordination?
Structure and functioning of a neuron. Reflex arc. Human brain. Chemical coordination in plants. Chemical coordination in humans.
What are the two types of control and coordination?
Nervous and Hormonal co-ordination.
What is the main controlling organ of the body?
The Brain.
.png)


PLEASE DO NOT ENTER ANY SPAM LINK IN THE COMMENT BOX